What is glutathione?
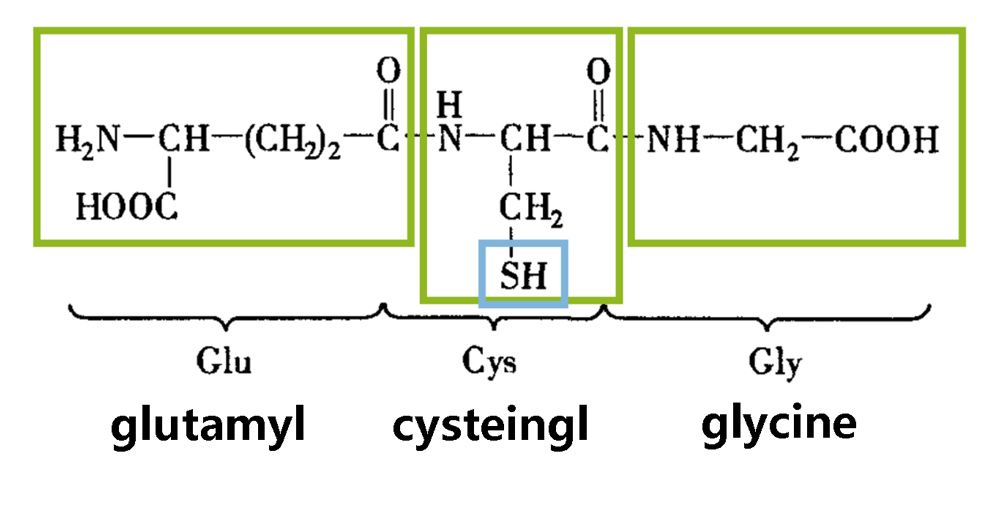
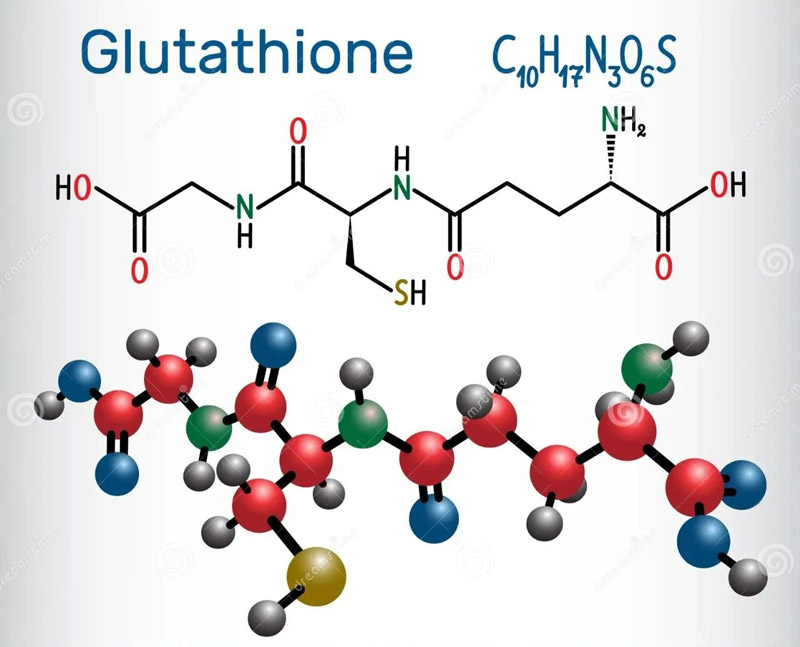
Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine, containing sulfhydryl group, which has antioxidant effect and integrated detoxification effect.
The thiol group on cysteine is the active group of glutathione, which is easy to combine with some drugs and toxins (such as free radicals, iodoacetic acid, mustard gas, lead, mercury, arsenic and other heavy metals), and has a broad spectrum detoxification effect.
Glutathione is found in almost every cell of the body, helps maintain normal immune system function, and has antioxidant effects.
There are two forms of glutathione, reduced and oxidized, and most of them are reduced glutathione under physiological conditions.
What is glutathione reductase?
GlutathioneReductase (GR) is an important cellular antioxidant in vivo, widely existing in human liver, kidney, cardiac erythrocytes, mononuclear macrophages and other tissue cells.
Its main physiological function is the main flavase to maintain the content of reduced glutathione (GSH) in cells.
It is of great value to protect the natural activities of sulfhydryl proteins and enzymes and the integrity of liver cell membrane.
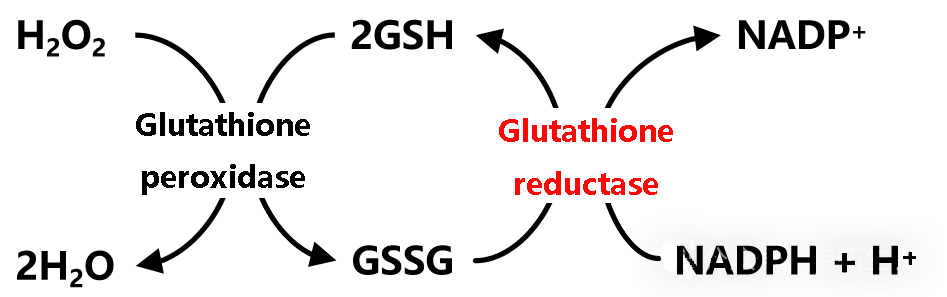
Glutathione reductase catalyzes tautomerism between the two types. When a small amount of H2O2 is produced in the cell, GSH reduces H2O2 to H2O under the action of glutathione peroxidase, and itself is oxidized to GSSG, and GSSG receives H+ to be reduced to GSH under the action of glutathione reductase, so that the free radical scavenging reaction in the body can be continued.
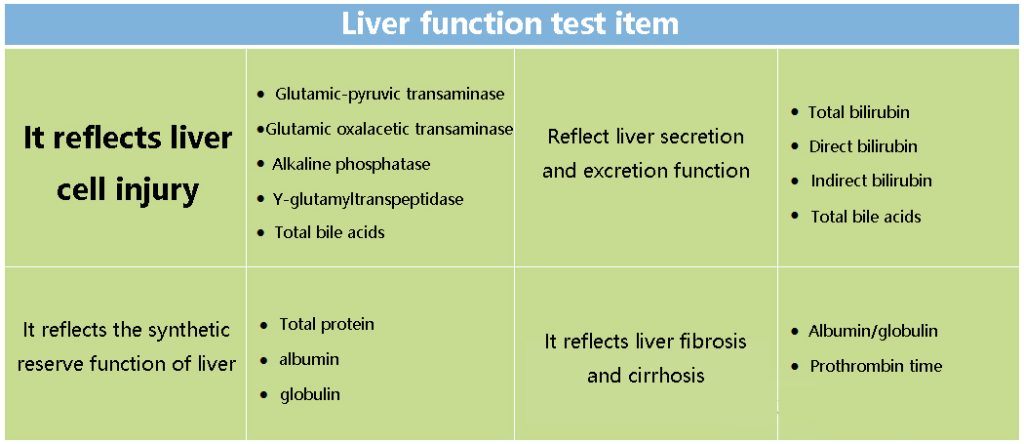
Liver function test item
Clinical significance of glutathione reductase
(1) GR was detected earlier than transaminase
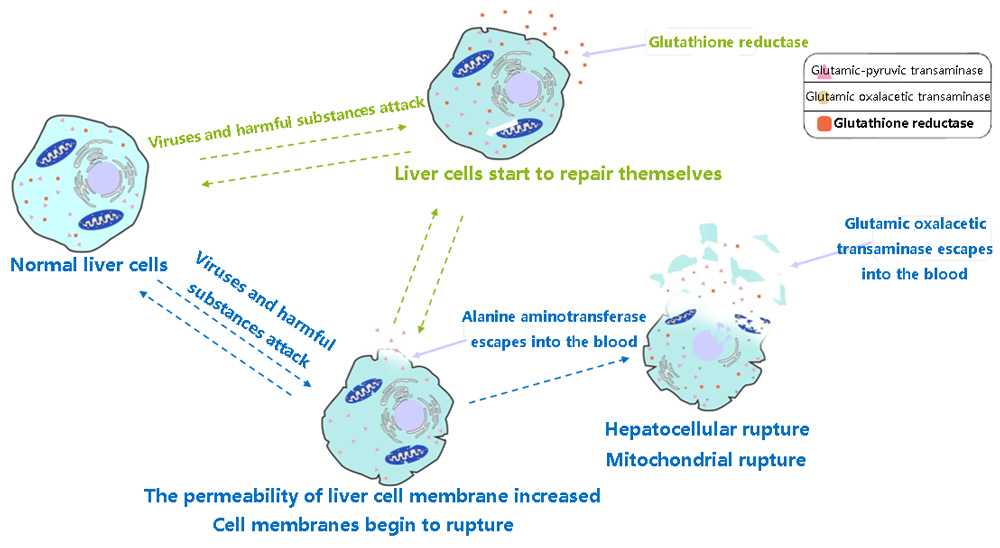
ALT and AST escape when the liver cell membrane and mitochondria rupture, respectively, and can detected in serum.
However, when liver cells damaged but permeability has not reached the state of rupture,
ALT and AST will not released into the blood, and early cell damage will not detected.
In the early stage of liver cell invasion by harmful substances and viruses,
GR produced in large quantities in the body and participates in the repair process of liver cell membrane.
GR detection is of great significance in the early stage of liver injury.
(2) The change degree of serum GR activity was large
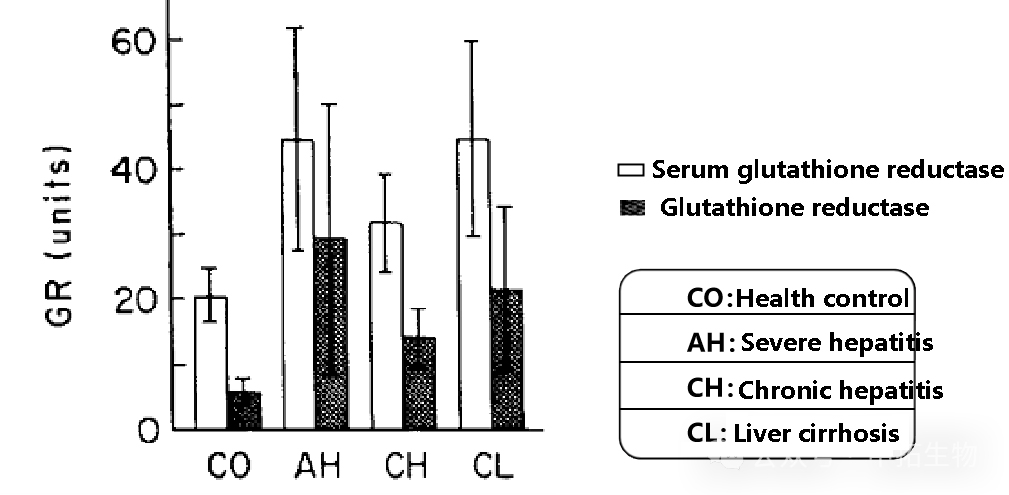
Compared with the GR activity in liver, the GR activity in serum increased more significantly.
(3) Early stage of acute hepatitis
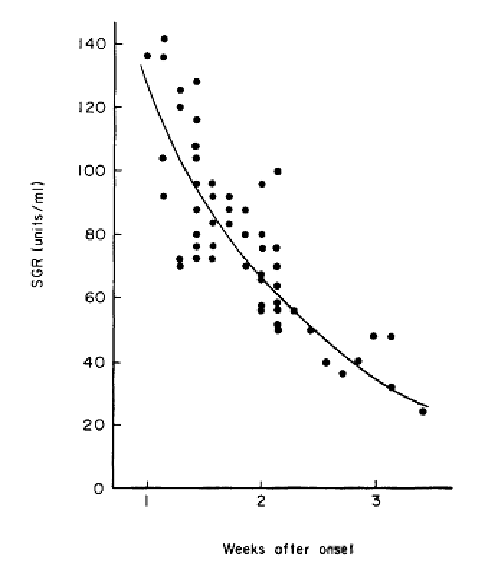
The results showed that in the early stage of acute hepatitis, SGR abnormally elevated in all patients.
Within 2-3 weeks of disease onset, 85.7% of patients were abnormal.
50% of patients are abnormal within 21-24 days.
Clinical studies have shown that the sensitivity of SGR is the highest in the early stage of acute hepatitis,
which can well reflect the change of the disease from occurrence to cure,
indicating the importance of continuous monitoring of SGR.
Therefore, GR can used to assist the diagnosis of acute hepatitis in liver parenchymatous lesions.
(4) Drug-induced liver injury

Glutathione can clear oxygen free radicals formed by chemotherapy drugs, or combine with therapeutic drugs and their metabolites to form low-toxicity products, protect or restore liver cell function.
Evaluating the GSH content by detecting GR activity is of great value in guiding the disease condition and monitoring the therapeutic effect of drug-induced hepatitis.
(5) Clinical interpretation
In Clinical Hepatology Trial Diagnostics and Clinical Test Diagnosis Analysis,
it clearly indicated that serum glutathione reductase activity can used to assist in the diagnosis of liver disease.
It should noted that the active reaction of GR usually in the early stage of cell damage, which should analyzed in various aspects, and it cannot found that the rise of GR defined as early hepatitis.
Glutathione reductase assay
(1) Physiological elevation:
Strenuous exercise:
Intense exercise can significantly increase GR, and the recovery of GR during exercise slow, and the GR activity still increased by 30%-50% after stopping exercise for 1H.
Intense exercise should avoided before GR measurement to avoid the increase in GR caused by activity, which will affect the correct interpretation of the measurement results.
Meals:
There are individual differences in the influence of eating on GR, and a few people can slightly increase the GR activity after eating.
The accuracy of GR results should avoided by fasting or two hours after eating before detecting GR.
Alcohol consumption:
After alcohol intake, it varies from person to person, and a certain amount of alcohol intake will cause an increase in GR activity.
Newborns:
The GR level will increase, which is 1 to 3 times higher than that of normal adults, mainly due to jaundice, and can decrease to the normal adult level in 3-6 months after birth.
(2) Drug interference:
Drugs that increase GR: chlorpromazine, isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, phenobarbital, morphine, painkillers and some lipid-lowering drugs
GR inhibitors: reduced glutathione injection and tablet.
(3) Genetic factors:
In patients with primaquine, glutathione reductase inhibited due to glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (fava disease) deficiency, which does not reduce sufficient amounts of NADPH.
(4) Others:
GR level inhibited by peroxide storage due to low glutathione concentration.