Japan completes clinical trials of NMN intravenous injection: significantly reduces blood lipids and is safe and reliable
Numerous clinical trials have confirmed that oral NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) can safely and effectively increase NAD+(nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) levels and improve various symptoms caused by aging.
Although intravenous injection of nicotinamide mononucleotide still commonly used in animal experiments to enhance NAD+levels,
the safety of this method for humans remains to confirmed.
In September 2022, a clinical trial conducted by a Japanese research team confirmed the safety and efficacy of intravenous injection of NMN,
which published in the journal Cureus.
In this clinical trial, researchers selected 10 healthy participants. After 12 hours of fasting, the subjects given 300mg of nicotinamide mononucleotide intravenously within 20 minutes and underwent a series of health indicator tests for the next 5 hours.
The results showed that intravenous injection of NMN can increase the level of NAD+in the blood within 2 hours without any adverse reactions.
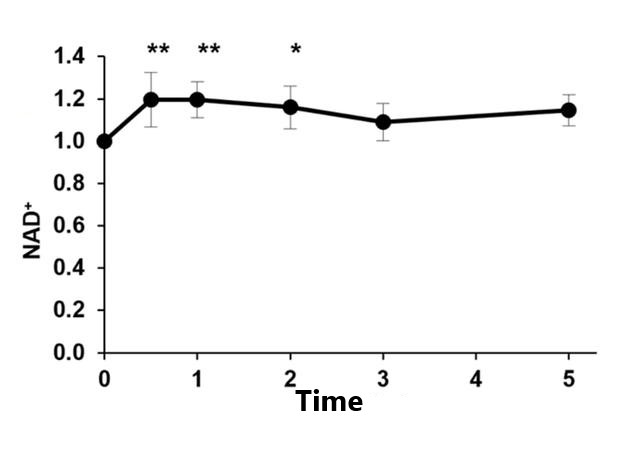
Moreover, intravenous injection of NMN can significantly reduce the levels of triglycerides (TG) in the blood,
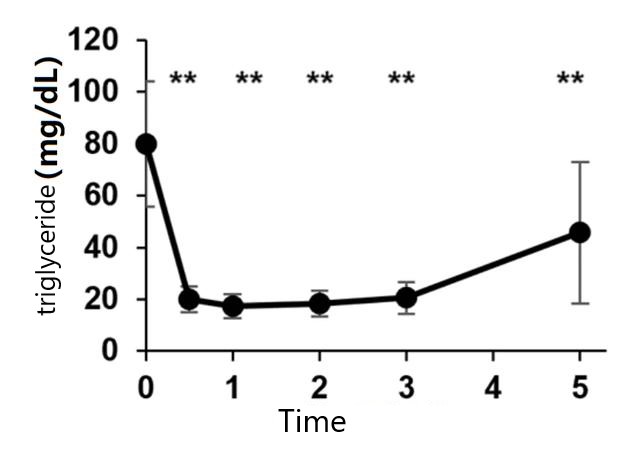
a phenomenon that has never observed in previous oral clinical trials.
How does NMN reduce triglycerides? This may be related to the action of adiponectin.
Adiponectin is a hormone secreted by adipocytes that can reduce the content of free fatty acids (FFAs) in the blood,
which are the raw materials for the liver to synthesize triglycerides.
After intravenous injection of NMN,
the level of NAD+in the blood increases and activates an enzyme SIRT1 that regulates cell health.
Researchers speculate that it is SIRT1 that promotes the action of adiponectin,
reducing free fatty acids in the blood, thereby inhibiting the synthesis of triglycerides in the liver and achieving the effect of lowering blood lipids.
In summary, this clinical trial confirmed the safety of intravenous injection of NMN and found that in addition to effectively increasing the level of NAD+in the blood,
it also has the effect of reducing triglyceride levels.
This will enable people in the future to have more ways to supplement NMN to meet the needs of different populations.
Reference:
1.Kimura, S., Ichikawa, M., Sugawara, S., Katagiri, T., Hirasawa, Y., Ishikawa, T., Matsunaga, W., & Gotoh, A. (2022). Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Is Safely Metabolized and Significantly Reduces Blood Triglyceride Levels in Healthy Individuals. Cureus, 14(9), e28812.