Comparative analysis of the therapeutic effect of citicoline and cerebral actin in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia
Research introduction citicoline
In this study, the efficacy of citicoline and cerebral actin in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia was compared.
Through the randomized treatment of 60 patients with cerebrovascular diseases, the results showed that both of them had a certain effect on improving the neurological function of cerebrovascular diseases, but cerebrovitrin showed a significant advantage in the treatment of vascular dementia.
This study also provides a valuable reference for further exploring the role of brain metabolic activators in the treatment of nervous system diseases.
Future studies can further explore the factors such as the mechanism of action, optimal dose and duration of the two drugs, so as to optimize the treatment plan and improve the quality of life of patients.
Citicoline and cerebral actin have their respective advantages in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia, and should be rationally selected and applied according to the specific conditions and characteristics of patients.
Part 1 Research background citicoline
The purpose of this study was to further compare the efficacy of citicoline and Cerebrolysin in the treatment of cerebrovascular disease and vascular dementia.
Cerebrovascular disease, as a common neurological disease, includes cerebral thrombosis, lacunar infarction, cerebral hemorrhage and other types, which not only pose a serious threat to patients’ life safety, but also may lead to serious long-term disability.
Vascular dementia, as a common complication of cerebrovascular disease, further aggravates the physical and mental burden of patients.

By comparing the efficacy of the two drugs, it can provide a more effective drug choice for clinical treatment.
Part 2 Materials and methods
In this study, patients with cerebrovascular disease and vascular dementia were randomly divided into two groups: citicoline group and cerebrovitrin group.
Each group of patients should be as balanced as possible in terms of age, sex, disease severity, etc., to ensure the accuracy of the test results.
Before the trial begins, all patients will undergo a comprehensive physical examination and neurological function assessment to determine the type and severity of the disease.
The two groups of patients will receive citicoline and encephalitin respectively.
The duration of treatment should be determined according to the pharmacological characteristics and clinical practice of the specific drug, and it is generally recommended to last at least several weeks to several months.
During treatment, patients will receive regular follow-up and evaluation to monitor the progression of the disease and the efficacy of the drug.
Evaluation indicators should include neurological function score, daily living ability score, cognitive function score, etc., to fully reflect the overall condition of patients.
Part 3 Research results
After treatment, we can compare the efficacy of the two drugs from the following aspects.
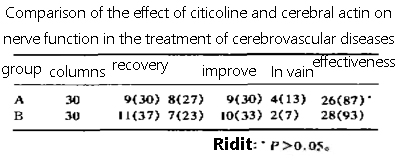
Neurological function improvement: By comparing neurological function scores before and after treatment between the two groups of patients, the degree of improvement in neurological function between the two drugs can be assessed.
If the neurological function score of the patients in the cerebral actin group was significantly higher than that in the citicoline group, it could be considered that cerebral actin was superior to citicoline in improving nerve function.
Improved daily living ability: The daily living ability score reflects the patient’s ability to live independently.
If the score of daily living ability of patients in the cerebral actin group was significantly higher than that in the citicoline group, it could be considered that cerebral actin was superior to citicoline in improving patients’ daily living ability.
Cognitive function improvement: The cognitive function score can reflect the patient’s cognitive function such as intelligence level and memory.

If the cognitive function scores of patients in the brain hormone group were significantly higher than those in the citicoline group, it could be considered that brain hormone was superior to citicoline in improving cognitive function.
Part 4 Research and discussion
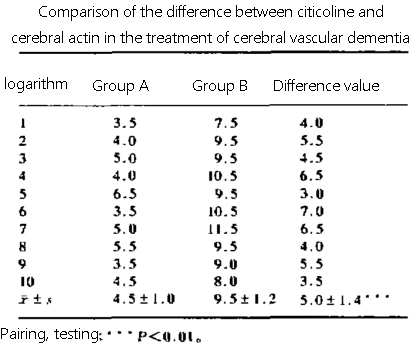
In this study, the efficacy of citicoline and cerebrovitrin in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia compared, and the results showed that cerebrovitrin may have unique advantages in the treatment of vascular dementia.
This finding has important significance for improving the treatment effect of vascular dementia.
In discussing this result, we note that encephalitin may have a positive effect on vascular dementia through its unique pharmacological mechanism of action.
As a nerve growth factor, encephalitin can promote the survival, growth and differentiation of nerve cells,
improve brain microcirculation, increase cerebral blood flow, and thus help improve cognitive function and nerve function.
In contrast, although citicoline also has a certain neuroprotective effect, its mechanism of action may be relatively simple,
and the therapeutic effect on vascular dementia may not be as significant as that of cerebrovitrin.
It is also important to note that the therapeutic effect of brain activation can influenced by a number of factors.
For example, the age of the patient, the course of the disease,
the severity of the disease and other factors can affect the efficacy of the drug.
In future studies, we need to further explore the impact of these factors on the efficacy of brain activation therapy to more accurately assess its efficacy.
Looking forward to the future, we can expand and deepen this research from the following aspects:
Study on mechanism of action:
Further study on the mechanism of action of cerebral cytokines in the treatment of vascular dementia,
including how it promotes the survival, growth and differentiation of nerve cells, and improves the microcirculation in the brain.
This will help us to more fully understand the therapeutic effects of brain activation and provide stronger support for its clinical application.
Combined application study: To explore the effect of the combined application of brain activating hormone with other drugs.
Through the synergistic effect with other drugs,
it may further improve the therapeutic effect of brain activation hormone and provide more effective programs for clinical treatment.
For example, the combination of brain cytokines with antioxidants, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.,
may better protect nerve cells from damage and improve cognitive function.
Study on comprehensive treatment measures:
Pay attention to the importance of comprehensive treatment measures in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia.
In addition to drug therapy, rehabilitation therapy and psychological intervention are also important means of treatment.
Future studies can further explore the effect of these treatments in combination with drug therapy to develop a more comprehensive and effective treatment plan.
Personalized treatment research: According to the specific conditions and physical conditions of different patients, develop personalized treatment plans.
Through in-depth understanding of the patient’s age, course of disease, severity and other factors,
we can provide patients with more accurate and effective treatment.
This will help improve the effectiveness of treatment and reduce the cost of treatment.
In conclusion, this study provides a new idea and method for the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia.
Future studies can further expand and deepen the results of this study to provide more comprehensive and effective treatment for patients.
Part 5 Research conclusion
By comparing the efficacy of citicoline and cerebral actin in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia,
we can provide a more effective drug choice for clinical treatment.
If the efficacy of encephalitin is superior to that of citicoline on several evaluation indicators,
then we can think that cerebral actin is a better choice for the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia.
It should noted that the specific illness and physical condition of different patients may different,
so in practical application, it should selected and adjusted according to the specific situation of patients.
The results of this study need to further validated and improved in future clinical practice.
By accumulating more clinical data and experience, we can more accurately evaluate the efficacy and safety of the two drugs,
and provide a more reliable basis for clinical treatment.
References:
[1] WANG Ximing, Sun Jiantian, Chen Huafeng, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of citicoline and cerebral actin in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia [J]. New Drug and Clinic,1996,(04):53-54.
Research review citicoline
This study has made a detailed comparative study on the efficacy of citicoline and cerebrovitrin in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia,
which has significant academic value and practical significance.
The following is a review of the study: Rigorous study design:
A randomized controlled trial used to ensure the objectivity and accuracy of the study results.
Through randomization, the influence of patient age, gender,
disease severity and other factors on the study results reduced to the greatest extent,
and the reliability of the study improved.
Comprehensive: The study not only looked at neurological improvements, but also included assessments of daily living and cognitive function.
This comprehensive evaluation method can more accurately reflect the therapeutic effect of the two drugs,
and provide a more comprehensive reference for clinical treatment.
Findings of value: The results of the study showed that cerebrovitrin has a significant advantage over citicoline in the treatment of vascular dementia,
and this finding has important significance for improving the treatment effect of vascular dementia.
This also provides a new way of thinking and direction for clinical treatment.
Reasonable recommendations: Based on the results of the study,
the study proposed reasonable selection and application of two drugs for different patients and disease characteristics.
This personalized treatment plan helps to improve treatment outcomes and reduce treatment costs.
The future research direction is clear: the study not only summarizes the current research results,
but also puts forward the direction of future research, including the exploration of the mechanism of drug action,
the optimal dose and course of treatment, and the combined use of other drugs.
These research directions are helpful to promote further research and development in related fields.
Limitation analysis: Although the research design is rigorous and the evaluation indicators are comprehensive, there are still some limitations.
For example, the relatively small sample size of the study may affect the generalizability of the results;
The effect of individual differences on drug efficacy not discussed. Future research could address these limitations.
In this study, the efficacy of citicoline and cerebrovitrin in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia deeply compared,
and valuable conclusions drawn, and reasonable treatment suggestions and future research directions put forward.
This study is of great significance for improving the therapeutic effect of cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia, and is worthy of further promotion and application.