Original price was: ¥280.00.¥255.00Current price is: ¥255.00.
CAS 53-84-9 Purity 99% Beta-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide NAD+ Powder
Customization: Available
CAS No.: 53-84-9
Formula: C21h27n7014p2
Get samples of US$ 0/gram
Total Plate Count: Maximum 1000cfu/G
HS Code: 29389090
Description
CAS 53-84-9 Purity 99% Beta-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide NAD+ Powder
Basic Info
β-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) |
|
| CAS | 53-84-9 |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Purity | ≥99.0% |
| Loss on drying | Not more than 8% |
| Heavy Metal | Not more than 10ppm |
| Application | Raw material, medicine |
| Shelf Life | 24 months when properly stored. |
| Molecular weight | 663.43 |
| Application | Dietary supplement ingredients |
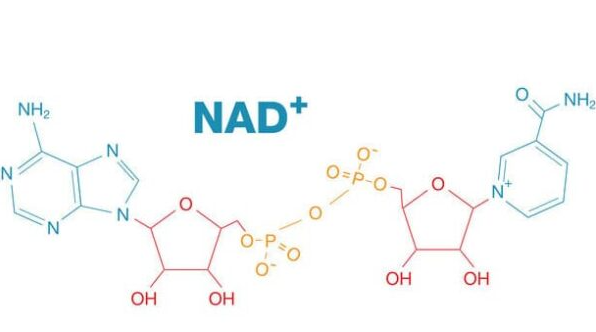
What is NAD+?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide.
NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively.
In cellular metabolism, NAD is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another, so it is found in two forms: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent, accepting electrons from other molecules and becoming reduced; with H+, this reaction forms NADH, which can be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons.
These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. It is also used in other cellular processes, most notably as a substrate of enzymes in adding or removing chemical groups to or from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.
In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building blocks from either tryptophan or aspartic acid, each a case of an amino acid. Alternatively, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from nutritive compounds such as niacin; similar compounds are produced by reactions that break down the structure of NAD, providing a salvage pathway that recycles them back into their respective active form.
Some NAD is converted into the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), whose chemistry largely parallels that of NAD, though its predominant role is as a coenzyme in anabolic metabolism.
In the name NAD+, the superscripted plus sign indicates the positive formal charge on one of its nitrogen atoms.
Features of β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+):
Coenzyme redox pair
NAD+ and its reduced form, NADH, are a coenzyme redox pair that participate in many enzyme-catalyzed oxidation reduction reactions.
Oxidizing agent
NAD+ is a vital small molecule that acts as an oxidizing agent in cellular metabolism. It regulates glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
ADP-ribose donor
NAD+ and NADH donate ADP-ribose units in ADP-ribosylaton reactions, and they are precursors of cyclic ADP-ribose.
Enzyme and metabolite determination
NAD+ used to determine enzymes and metabolites such as amylase, creatine kinase, transaminases, lactate dehydrogenase, phosphohexose isomerase, ethanol, galactose, glucose, uric acid, L-lactate, and triglycerides.
Neurotransmitter
NAD+ may contribute to enteric inhibitory regulation of visceral smooth muscles. Inhibitory neurons are essential for complex motor patterns like peristalsis, receptive relaxation, and sphincter opening.
NAD+ made up of two nucleotides, one with an adenine base and the other with a nicotinamide base, joined by phosphate groups. It’s a white solid or powder that’s highly hygroscopic.
Additional information
| brand | GSHWORLD |
|---|









Was a pleasure to do businesses with. Customized to my specification. Quality as agreed. delivered on time.