Scientists have made some progress in finding effective ways to mitigate lung damage caused by cigarettes, among which NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) has attracted a lot of attention as an important coenzyme.
Smoking is still a significant contributor to many diseases, especially lung disease.
Studies have shown that harmful substances in cigarettes can cause significant damage to lung tissue, which can lead to serious diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer.
The damage of cigarettes to the lungs
Smoking is one of the major risk factors for many lung diseases.
Thousands of chemicals are produced when cigarettes are burned, including harmful substances such as nicotine, tar and carbon monoxide. When these substances enter the lungs, they cause a series of pathological changes.
Nicotine damages the cilia of the bronchial mucosa, reducing its ability to clear foreign objects from the respiratory tract.
Tar deposits in lung tissue, damaging the structure and function of the alveoli.
Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin, reducing oxygen delivery and causing tissue hypoxia.
Long-term smoking can also cause serious diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer.
The magic of NAD+
NAD+ is a molecule that plays a crucial role in cell metabolism. It is involved in many important physiological processes such as energy metabolism, DNA repair and cell senescence.
The researchers found that NAD+ also had a significant effect in reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory responses.
In studies of lung damage caused by cigarettes, scientists have found that NAD+ can play a protective role in a number of ways.
On the one hand, NAD+ can activate the antioxidant oxidase system in cells, enhance the antioxidant capacity of cells, and reduce the damage of free radicals to lung tissue.
On the other hand, NAD+ can also inhibit the release of inflammatory factors and reduce the inflammatory response in the lungs.
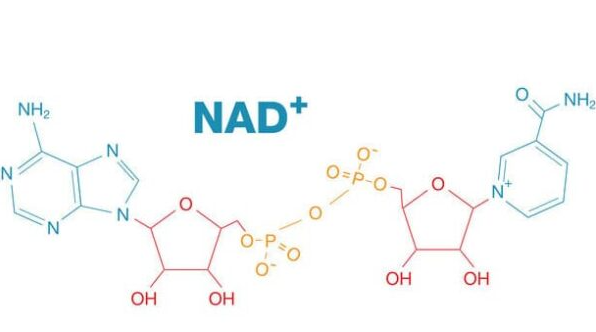
β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide can also promote the repair and regeneration of lung cells. It activates a protein called SIRT1, which plays a key role in cell aging and repair.
SIRT1 can promote autophagy of lung cells, remove damaged organelles and proteins, and create a good environment for cell repair and regeneration.
Research progress and results
To verify the protective effect of NAD + on smoking-induced lung damage, the scientists conducted a series of animal and cell experiments. In animal experiments, the researchers exposed mice to cigarette smoke while giving NAD+ supplements.
The results showed that compared with mice that did not receive NAD+ supplementation, mice that received NAD+ supplementation had significantly reduced lung inflammation and significantly improved lung function.
In the cell experiment, the researchers exposed lung cells to cigarette smoke extracts and observed the effects of NAD+ on the cells.
The results showed that β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide can reduce cell death and oxidative stress caused by cigarette smoke extract and protect the integrity of lung cells.
In July 2020, several scholars from Southern Medical University accidentally found that the root cause of lung injury from smoking was the decline in β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide levels when studying the hazards of smoking, and sorted out the related physiological processes.
According to this physiological process, several scholars have confirmed that enhancing the level of NAD+ in lung cells by supplementing the body’s β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide can greatly restore the autophagy function of cells, reduce the number of senescent cells, and reduce the incidence of lung diseases.

These research results provide an important theoretical basis for the development of new therapeutic methods and drugs.
We are expected to reduce lung damage caused by cigarettes by supplementing NAD+ or developing drugs that activate β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide synthesis, providing better protection for the lung health of smokers and passive smokers.”
How to supplement NAD+
There are two main ways to supplement NAD+ : dietary supplementation and supplement supplementation.
Some foods are rich in NAD+, and by ingesting these foods, the level of NAD+ in the body can increased to a certain extent. Common foods rich in β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide are meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, etc.
There are also some NAD+ supplements available on the market. When choosing NAD+ supplements, we should be careful to choose regular products and use them under the guidance of a doctor.

Appeal and prospect
The harm of smoking to health cannot ignored, and it is particularly important to find effective intervention measures.
As a potential protective factor, NAD+ provides a new way to reduce lung damage caused by cigarette smoke.
Future studies will further reveal the mechanism of action of NAD+ in lung health and provide more effective means of protection for smokers.
As a potential lung health protective molecule, NAD+ deserves our further research and attention. It is believed that in the near future, it will bring new breakthroughs in our fight against lung damage caused by cigarettes.