In recent years, scientific research has found that a substance called NMN (β-nicotinamide mononucleotide) has shown great potential in reversing intestinal aging.
As the main digestive organ and the largest immune organ of the human body, the health of the gut is directly related to our overall physical and mental health.
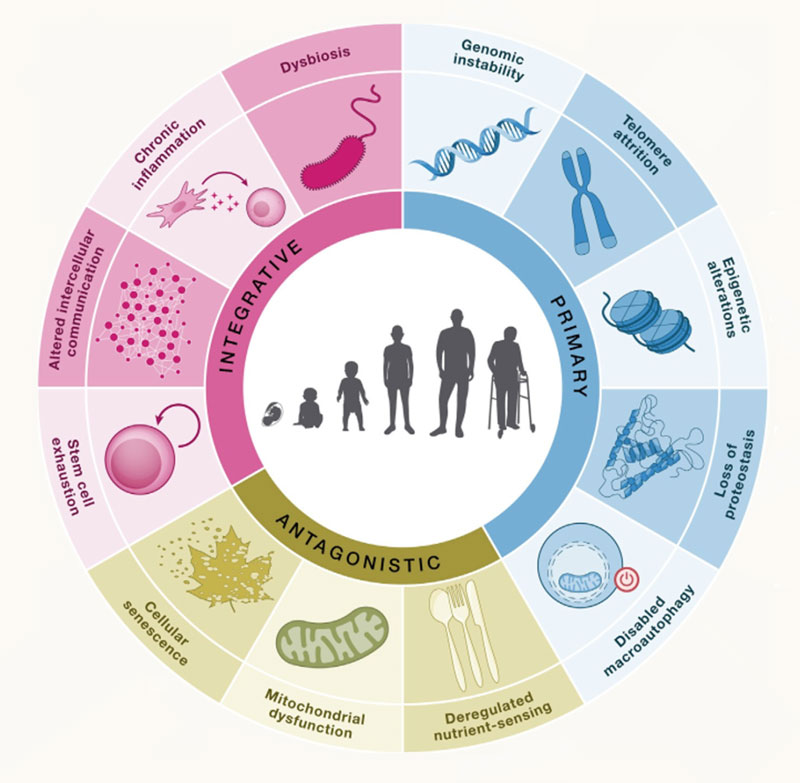
With the increase of age, the gut will gradually age, which is manifested by decreased intestinal function, microbial imbalance and weakened digestive ability.
Mitochondrial DNA mutation and intestinal aging
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations are one of the important causes of aging and age-related diseases.
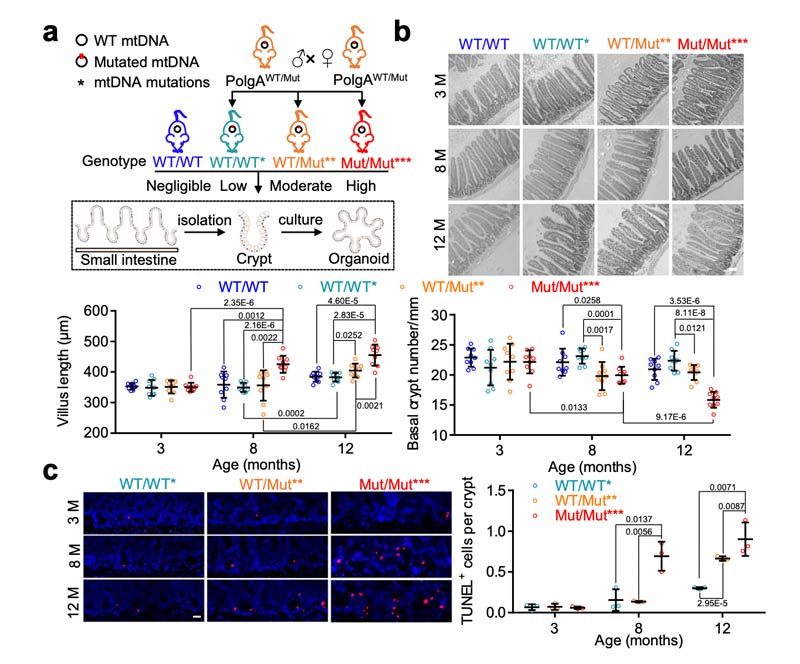
In the small intestine and other organs, the increase of mtDNA mutation induces the senescence phenotype, such as a decrease in the number of intestinal crypts, an increase in villi length, and an increase in the expression of aging marker CDKN1A/p21.
These changes not only affect digestion, absorption and immune function in the gut, but can also lead to dysregulation of gut microbes and mitochondrial dysfunction, which in turn can negatively impact overall health.
NMN: Increase the level of NAD+ and reverse intestinal aging
NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is an important coenzyme in cells that participates in a variety of biochemical reactions and is essential for maintaining cell metabolism and survival.
Studies have shown that mtDNA mutations lead to NAD+ depletion during intestinal aging.
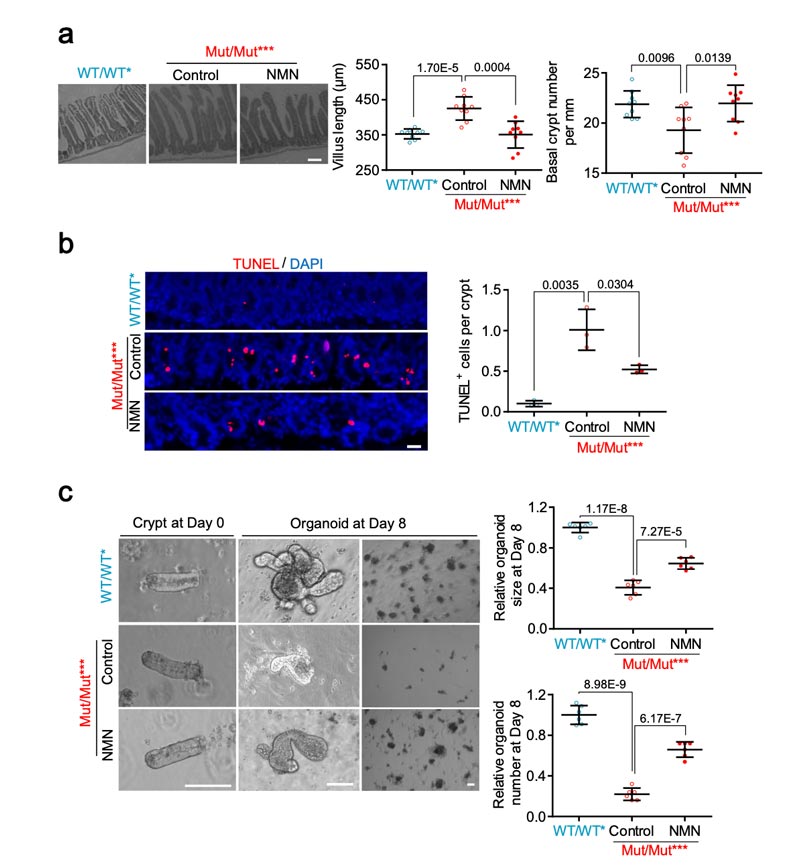
Supplementation of NAD+ precursor NMN can increase the level of NAD+, thereby reversing the aging of the small intestine caused by mtDNA mutations.
Experiments in mice showed that the number of intestinal crypts increased and villi length decreased after NMN supplementation, which alleviated the small intestinal aging phenotype caused by mtDNA mutation load.
This suggests that the loss of NAD+ is the key to inducing small intestine aging, and the supplementation of NMN can save the aging of the small intestine.
NMN is also able to regulate the intestinal flora, manifested by an increased abundance of beneficial bacteria and a decreased abundance of harmful bacteria, helping to restore intestinal colonization resistance and improve overall intestinal health.
Other benefits of NMN
In addition to reversing intestinal aging, NMN has been found to have a variety of other benefits.
For example, it can protect intestinal stem cells, rejuvenate them, and save colon degeneration in older rodents.
NMN also increases the activation of genes associated with antioxidants, such as SOD2 and Nrf2, and decreases the expression of genes associated with inflammation, thereby inhibiting the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), reducing inflammation, and improving antioxidant capacity.
These findings further confirm the positive role of NMN in anti-aging and improving health.
Clinical application prospect of NMN
With the deepening of research on NMN, its application prospect in reversing intestinal senescence and other age-related diseases will be broader.
Clinical trials in women have shown Nicotinamide Mononucleotide to be excellent at improving gut health.
In particular, the composite NMN greatly improves the conversion efficiency of NAD+, and changes the disadvantages of traditional Nicotinamide Mononucleotide products with low absorption and single action.
As more clinical trial results are published, NMN is expected to become the choice of more people looking for a “long and healthy life.”
Conclusion
Intestinal aging is a complex process involving multiple biochemical reactions and molecular mechanisms.
As a new type of anti-aging substance, NMN provides a new hope for reversing intestinal aging by enhancing the level of NAD+, improving intestinal function and regulating intestinal flora.
With the continuous progress of scientific research and the in-depth development of clinical trials, it believed that NMN will make greater contributions to human health in the future.