Are they all exploding? NMN request to fight: female “beautiful”, male “handsome”, not not!
Recently, the entertainment industry has set off an unprecedented “explosion wind”.
Before the explosion of Jin Jing, from “funny girl” gorgeous change to “Korean female love beans”,
after Yang Di instant incarnated as a boy group high cold love beans,
this “changing head type” explosion effect let netizens call it unrecognizable.
However, in the pursuit of external beauty, inner health can not ignored. NMN, a molecule that plays an important role in living organisms, is attracting attention for its unique anti-aging charm.
Improvements NMN brings to women
As women age, they face many problems such as skin aging, loss of elasticity, wrinkles and sagging.
The β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide research has brought new hope for anti-aging and beauty for women.
A number of studies have shown that β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide can activate cellular energy,
protect skin cells from the external environment, reduce the production of melanin, and thus improve the state of the skin.

A study from a Japanese research team also found that in the combination of NMN,
eating a high-fat diet can easily lose weight, allowing those accumulated fat to voluntarily leave the field.
NMN has a positive impact on women’s reproductive health.
Professor Xiong Bo’s research team from Nanjing Agricultural University found that injecting NMN into mice can effectively improve the quality of senescent oocytes.
This will bring a very important reference significance for improving the fertility of older people parturients.
Improvement of NMN in men
For men, NMN has significant benefits. American scientific researchers have found that NMN can reverse the damage of alcohol to the liver,
reduce the content of aminotransferase in plasma, and help protect liver health.
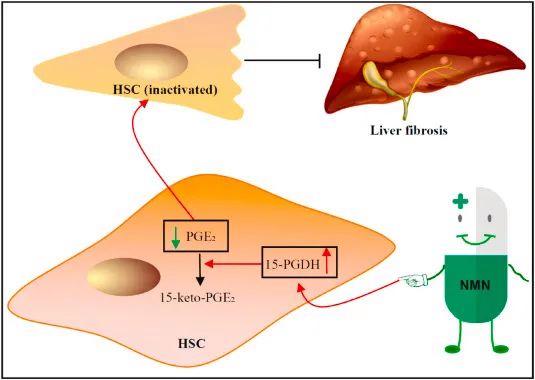
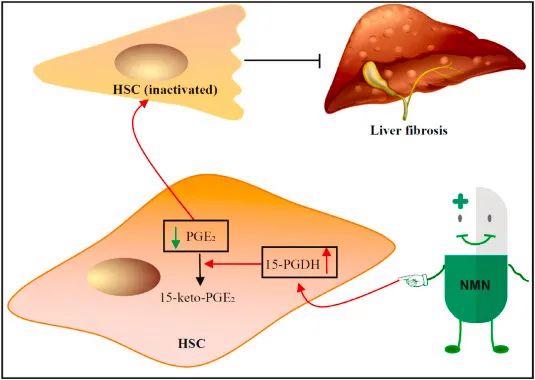
In addition, the research of Deng Haiteng research group at Tsinghua University confirmed that NMN can effectively prevent liver fibrosis and escort male liver health.
In terms of exercise, human trials at Guangzhou Sport University have shown that supplementing NMN can enhance the aerobic capacity of amateur runners and help improve athletic performance in men. This finding brings good news for many men who love sports, making them more energetic and attractive in sports.
To sum up, it not only brings the dual benefits of beauty and health for women, but also provides comprehensive health protection for men. With the continuous deepening of NMN research and the continuous expansion of application fields, it is believed that it will become a strong support for more people to pursue health and beauty.
reference
- [1]Chang TM, Yang TY, Huang HC, Nicotinamide Mononucleotide and Coenzyme Q10 Protects Fibroblast Senescence Induced by Particulate Matter Preconditioned Mast Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 7:23(14):7539.
- [2] Brito S, Baek JM, Cha B, Heo H, Lee SH, Lei L, Jung SY, Lee SM, Lee SH, Kwak BM, Chae S, Lee MG, Bin BH. Nicotinamide mononucleotide reduces melanin production in aged melanocytes by inhibiting cAMP/Wnt signaling. J Dermatol Sci. 2022 Jun: 106(3):159-169.