What is NAD+?
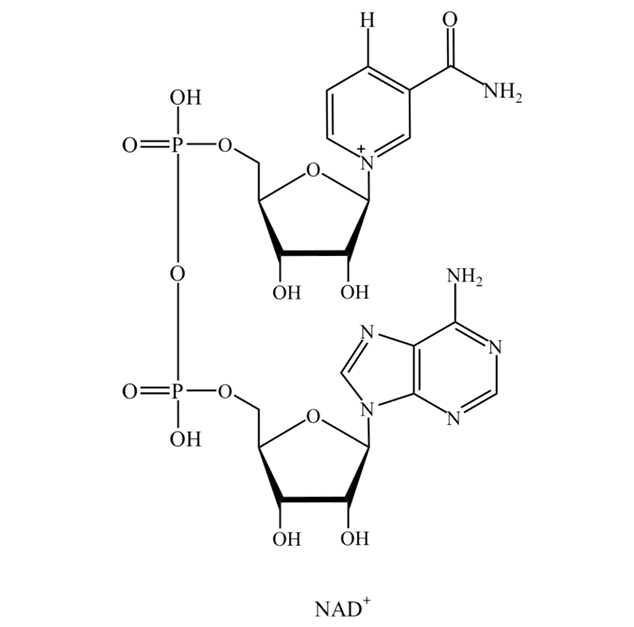
NAD+ Chinese name: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, referred to as coenzyme Ⅰ. It is derived from NMN, namely β-nicotinamide mononucleotide, which enters the human body and is converted by enzyme.
NAD+ is involved in thousands of cellular metabolic reactions and acts as a cellular “communicator.”
NAD+ is a key molecule that is ubiquitous in all human cells. As an indispensable cofactor of Sirtuins proteases and CD38 polymerase, NAD+ participates in and promotes the REDOX reaction.
NAD+ plays a central role in cellular energy metabolism, directly or indirectly regulating a variety of key cellular functions.
In short, without the involvement of NAD+, the cells will have difficulty producing the energy they need, leading to cell loss of vitality and the risk of apoptosis.
After long-term in-depth research, the mechanism of NAD+ in the field of anti-aging is gradually clear.
In particular, the research team led by Dr. Eric Verdin, director of the BUCK Institute, published a review article on the role of NAD+ in cell metabolism and aging in nature reviews, a subsidiary of the authoritative scientific journal nature.
In this paper, the important functions of NAD+ in cellular metabolic pathway, DNA repair mechanism, cellular immune regulation and aging process are comprehensively described, which provides a new perspective and ideas for anti-aging research.
Synthesis and metabolism of NAD+
1. Metabolic consumption of NAD+
NAD+ levels decline with age because it is involved in many important metabolic responses.
Mainly from three aspects:
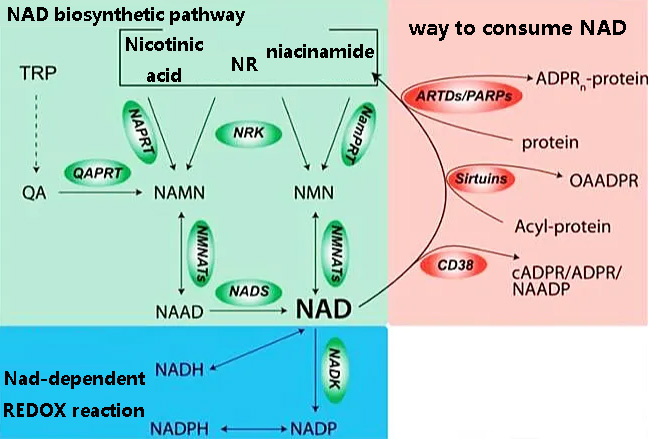
- (1) DNA damage accumulates with age. DNA damage activates the enzyme PARPs. PARPs consume NAD+ to repair damaged DNA.
- (2) Enzymes in the immune system also consume NAD+. The more active the immune system is, the more NAD+ it consumes.
- (3) There is an important class of enzymes called sirtuins, which play an important role in maintaining chromosome stability and DNA repair. DNA damage and chromosomal instability accumulate with age, causing sirtuins to consume more NAD+.
Among them, repairing DNA damage consumes the most NAD+.
2. Synthetic pathway of NAD+
There are two main ways to synthesize NAD+.
One is NMN synthesis.
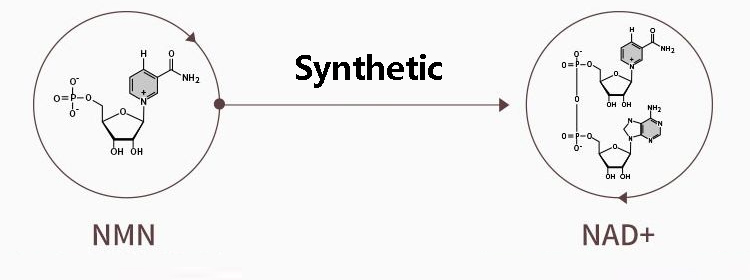
The Chinese name of NMN is β-nicotinamide mononucleotide.
NMN enters the human body and, with the help of the enzyme NMNAT, consumes a certain amount of energy (ATP) at the same time, and is eventually converted into the anti-aging factor NAD+ (coenzyme 1) to play a role in delaying aging.
One is the NADH decomposition method.
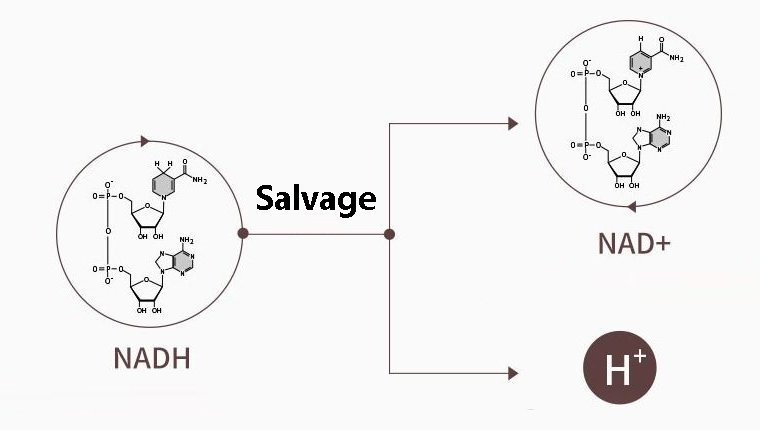
The Chinese name for NADH reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
NADH enters the human body and directly decomposed into NAD+ and hydrogen (H), while releasing a certain amount of energy (ATP). Under the synergistic effect of the three, NADH not only has a comprehensive anti-aging effect, but also performs well in enhancing immunity.
The two have in common that they are both precursors of NAD+, and their ultimate purpose is to provide the body with anti-aging factor NAD+.
The difference that NMN synthesized in the human body, while NADH decomposed into NAD+ in the human body.
Specific efficacy of NAD+
As an important coenzyme and energy producing medium, NAD+ has a great impact on many functions of the body.
(1) Improve the metabolic system
If the lack of NAD+ will first lead to human metabolic disorders, especially for the older people and higher-weight person people, it will lead to an increase in the probability of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, stroke, cancer and other diseases.
NAD+ can activate a variety of coenzymes, inhibit the growth of fat cells, promote metabolism, and maintain body health.
(2) Enhance cardiovascular function
High blood pressure can lead to an enlarged heart and blocked arteries, which can lead to stroke.
And raising NAD+ levels prevents damage to the heart caused by insufficient blood. It protects mice from abnormally enlarged hearts.
(3) Repair immune function
As the immune system declines with age, NAD+ plays an important role in regulating the immune system and inflammation.
Supplementation with NAD+ can regulate the activity of proteases such as CD38 and PARPs, resulting in the reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the restoration of immune function.
(4) Relieve neurodegeneration
In people with Alzheimer’s disease, increasing NAD+ levels can reduce the accumulation of harmful proteins and enhance the transmission of information between brain cells, thereby restoring brain cognitive function.
Boosting NAD+ levels also protects brain cells from death when there is not enough blood flow to the brain.
(5) Anti-aging prolongs life
Birth, old age and death are normal for human beings, and senescent cells will increase the secretion of SASP, interfere with stem cell regeneration, affect tissue repair and exacerbate cellular inflammation, resulting in continuous aging of cells and tissues.
The increase of NAD+ can promote cell metabolism, enhance mitochondrial function, enhance cell activity, and effectively delay aging.
Complementary mechanism of NAD+
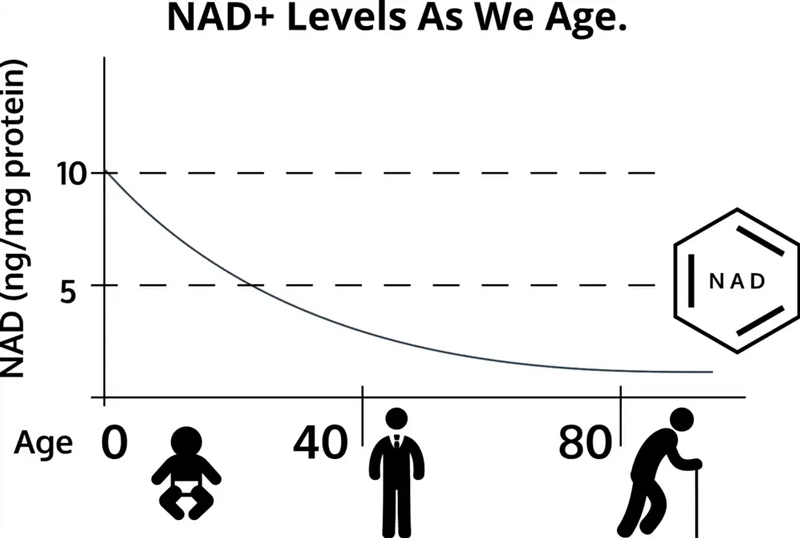
Professor David Sinclair of Harvard University, a global leader in anti-aging, has found that our NAD+ levels at age 50 are only half of what they were at age 20.
NAD+ plays an important role in maintaining cell activity and human health. If the human body compared to a car, NAD+ is fuel, and the car cannot run without fuel and loses its vitality.
Continuous supplementation of NAD+ is the primary issue of anti-aging, and you can start from the following four aspects to improve the level of NAD+ :
- Precursors such as NMN or NADH taken orally to directly supplement NAD+.
- By activating the activity of rate-limiting enzymes such as NAMPT and NMNATs, the reaction that naturally produces NAD+ in the body accelerated.
- NAD+ can be quickly and effectively supplemented by intravenous transfusion directly.
- Inhibits the rate at which enzymes such as PARPs and CD38 consume NAD+ in the body.
Prospect and exploration of NAD+
Comprehensive studies of NAD+ are continuing and have shown great potential for treating cardiovascular disease, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease and obesity, but there are still many mysteries to solved.
The aging of the global population is becoming more and more serious, anti-aging will become an extremely important topic, and the research on NAD+ will become the top priority, let’s wait and see.