NAD+ plays an integral role in the biology of aging.
In today’s society, aging has become a risk factor for many diseases, including diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative diseases, and complications following infections such as COVID-19.
Because of this, the scientific community is increasingly focusing on the effects of the physiology of aging and seeking to combat this physiological phenomenon through effective treatments.
NAD+ The key molecule of miracle life
A review published in Aging Cell on July 9, 2023, titled “NAD Metabolism: Its Role in Aging Regulation and Aging,” states:
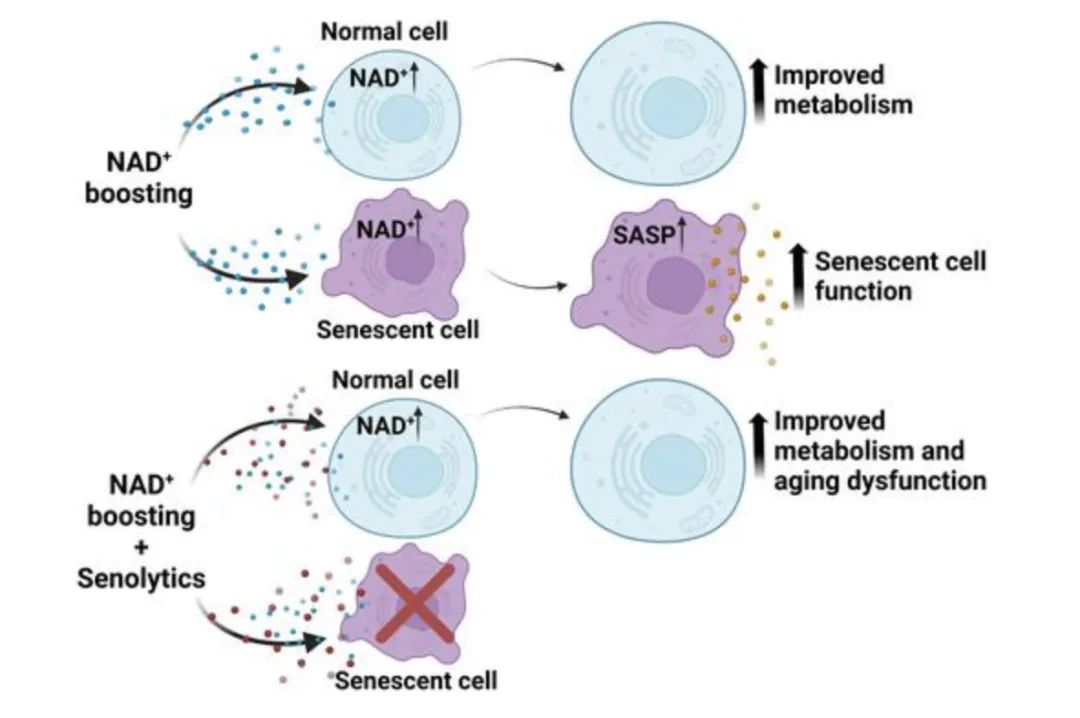
Several biological features of NAD+ and aging (including cellular aging) and changes in NAD metabolism have been shown to be associated with the aging process.
On the one hand, the accumulation of DNA damage and mitochondrial dysfunction induced by low NAD+ can promote the development of aging.
On the other hand, the low NAD+ state that occurs during aging may inhibit the development of SASP, since both this secretory phenotype and the development of cellular aging are metabolically demanding.

As early as 2021, the Barker Institute for Aging Research, which dedicated to anti-aging research, has detailed the role of NAD+ in metabolic pathways, DNA repair, cellular immunity, and aging.
Studies have shown that NAD+ can directly and indirectly affect a number of key cellular functions, including metabolic pathways, DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, cellular aging, and immune function, which are cellular processes essential for maintaining tissue and metabolic homeostasis and healthy aging.
NAD+ works as follows:
- ① Improve the metabolic system;
- ② Enhance cardiovascular function;
- ③ Repair immune function;
- ④ alleviates neurodegeneration;
- ⑤ Anti-aging to prolong life;

NAD+ is an important part of the metabolic pathway
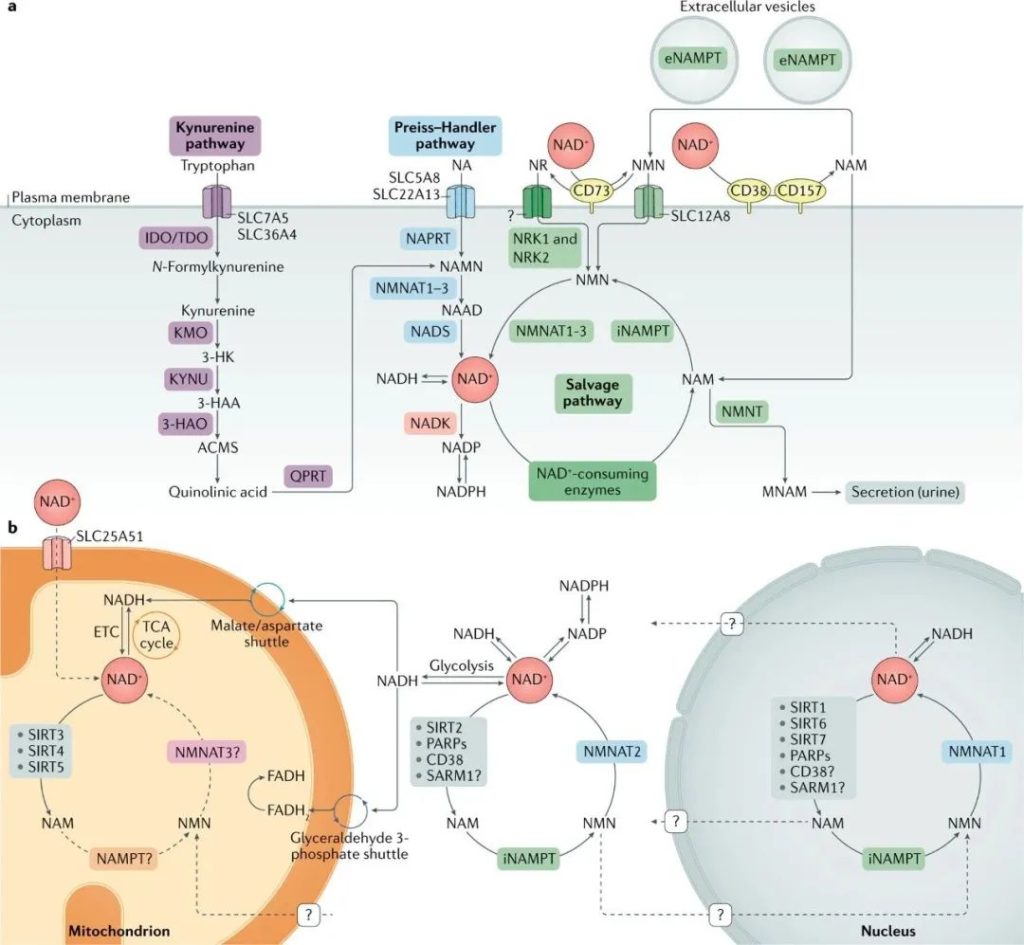
In glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle, NAD+ acts as an electron carrier, helps transfer and store energy, and supports the synthesis of ATP in the cellular mitochondria, which is the primary source of cellular energy.
NAD+ participates in the β-oxidation of fatty acids, promotes the decomposition and energy release of fats, and thus maintains the balance of cellular energy.
NAD+ supports protein synthesis and function maintenance by regulating the synthesis and degradation of amino acids and is essential for cell growth and repair. Together, these processes ensure the normal metabolic and physiological function of cells.
NAD+ is involved in maintaining REDOX homeostasis
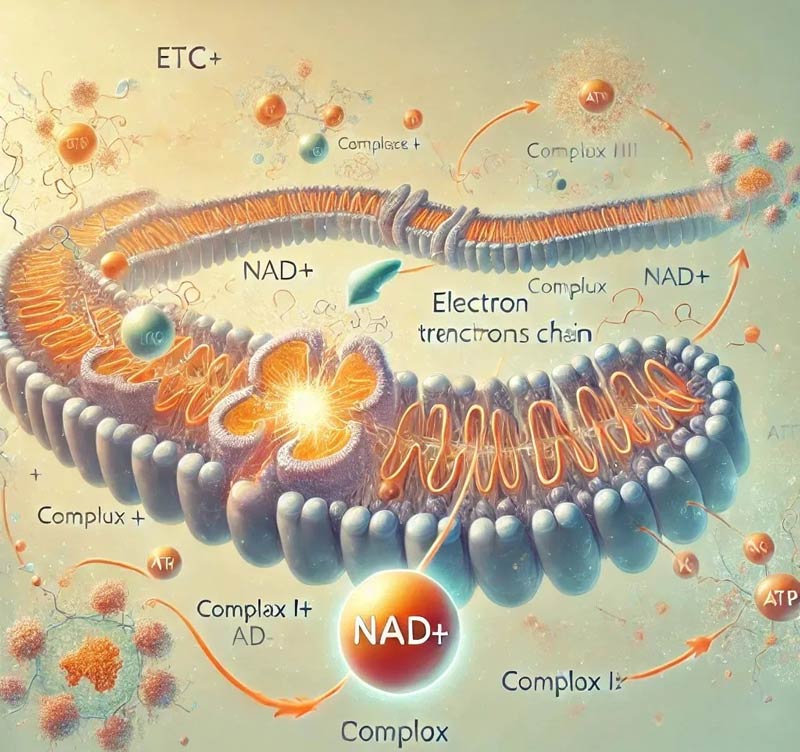
NAD+ plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell’s REDOX homeostasis, and it helps regulate the metabolic state of the cell by participating in REDOX reactions within the cell by accepting and releasing electrons.
This process is essential for maintaining the stability of the intracellular environment.
NAD+ also involved in the production of antioxidants, such as glutathione, which can effectively protect against oxidative stress and reduce free radical damage to cells, thereby protecting cell health and function.
Through these mechanisms, NAD+ plays an important role in maintaining the physiological state of cells and promoting cell survival.
NAD+ is involved in anti-inflammatory processes
NAD+ plays an important role in anti-inflammatory processes, especially in regulating the body’s immune response.
By modulating the activity of immune cells, NAD+ is able to effectively suppress unnecessary inflammatory responses, thereby reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
After tissue damage, increased levels of NAD+ help promote cell repair and regeneration, reducing the impact of inflammation on damaged tissue.
This mechanism makes NAD+ an important molecule for maintaining tissue health and promoting healing, offering a potential therapeutic strategy for tackling inflammation-related diseases.
NAD+ has anti-aging effect
NAD+ shows significant potential in anti-aging by activating genes associated with longevity, such as SIRT1, thereby promoting cell repair and maintaining metabolic homeostasis, delaying the aging process.
Adequate NAD+ levels help maintain mitochondrial health, promote efficient energy production, and enhance cell vitality.
NAD+ also effectively reduces the rate of cell aging and prolongs the survival time of cells by enhancing the DNA repair mechanism and enhancing the antioxidant capacity.
These functions make NAD+ an important molecule for studying anti-aging and prolonging healthy life.
By understanding the mechanism of action of NAD+, we can not only develop new anti-aging strategies, but also effectively prevent age-related chronic diseases.