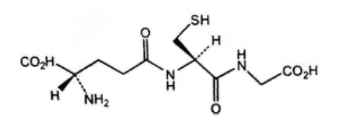
Glutathione is an important antioxidant in the human body, in the form of reduced glutathione (GSH) and oxidized glutathione (GSSG), of which GSH is composed of glutamic acid, glycine and cysteine through peptide bonding, and is synthesized in the liver in the largest amount.
Glutathione has many physiological functions
1, Antioxidant effect
Free radicals can damage cell membranes, and glutathione is able to help remove free radicals in the body, protecting the sulfhydryl groups in many proteins and enzymes and other molecules, so that cells from oxidative damage.
2, Improve liver function and treat various liver diseases
Glutathione can improve the antioxidant activity to promote the repair and regeneration of liver cells, while promoting the detoxification of the liver, which is conducive to the protection of the liver, but also reduce the damage of the cell membrane, and maintain the integrity and stability of the liver cell membrane.
Clinically, GSH is used as an important drug ingredient for liver protection.
Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of drug-induced Liver Injury (2023 edition) pointed out that GSH is one of the recommended therapeutic agents for mild and moderate hepatic cell damage type DILI (drug-induced liver injury) with elevated ALT (alanine aminotransferase) /AST (glutamic oxalacetic aminotransferase).
In addition, studies have shown that the combined application of glutathione in the treatment of viral hepatitis patients on the basis of conventional treatment can effectively improve the total effective rate of treatment.
Glutathione can also be used in alcoholic liver disease to accelerate free radical excretion and reduce liver cell damage.
3, Maintain immune function
Glutathione can regulate the activity of immune cells and enhance immunity.
Quickly identify and remove foreign pathogenic microorganisms.
It can also help promote the production of antibodies in the body and promote the normal operation of the immune response.
4, Protect hemoglobin
Under the oxidation of hydrogen peroxide and free radicals, the bivalent iron in some hemoglobin in red blood cells oxidized to trivalent iron, making hemoglobin become methemoglobin, and losing the ability to carry oxygen.
Glutathione can protect hemoglobin from oxidation such as hydrogen peroxide and free radicals, and continue to perform normal oxygen transport capacity.
5, It is effective for diabetic nephropathy
GSH can inhibit the progression of diabetic nephropathy by regulating the activity of alanine thionylase.
Glutathione can also reduce inflammation and reduce urinary microalbumin excretion, thereby delaying the development of diabetic nephropathy.
As an endogenous active peptide, GSH can effectively detoxify, reduce oxidative stress,
regulate immune response and control inflammation by eliminating or neutralizing various harmful peroxides and free radicals produced in the human body.
GSH has high clinical efficacy in the treatment of glomerulonephritis,
nephrotic syndrome, chronic kidney disease and chronic renal failure decompensated stage.
At present, glutathione commonly used in clinic, including tablets, injections and oral lozenges.
Despite the many benefits of glutathione, public health pharmacists caution that the following must be noted when using:
- Dosage is appropriate to avoid overdose.
Excessive amounts can lead to nausea, vomiting, etc., and may impair kidney function in severe cases.
- Be aware of drug interactions.
Glutathione may interact with some drugs, affecting the effect of drugs, should avoid simultaneous use.
- Use with caution for special groups.
For example, pregnant women, breastfeeding women, and people with certain medical conditions should consult a doctor before use.
- Regular monitoring.
Long-term use of glutathione should regularly checked to ensure that the intake is within a safe range and the body has no adverse reactions.
References:
- [1] Technical Committee of Prevention and Treatment of drug-induced Liver Injury, Chinese Medical Biotechnology Association, Drug Hepatology Group, Hepatology Branch, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of drug-induced liver injury (2023 edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Hepatology, 2023,31(4):355-384. (in Chinese)
- [2] Zhang Tao, Li Saishuai, Diao Qinfeng. Clinical efficacy of reduced glutathione in the treatment of viral hepatitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Pharmaceutical Application, 2019,15(14):129-131. (in Chinese)
- [3] LIU Yajuan, Li Xuesong, Li Qinyuan et al. Research progress of reduced glutathione in the treatment of immune-related diseases [J]. Journal of Practical Clinical Medicine,2016,20(17):205-208. (in Chinese)
- [4] Glutathione Instructions.




